
Microfocus netexpress free download. Our website provides a free download of Micro Focus Net Express 5.106.79. The most popular versions among Micro Focus Net Express users are 5.1, 4.0 and 3.1. The most popular versions among Micro Focus Net Express users are 5.1, 4.0 and 3.1. Net Express® (for Windows) and Server Express™ (for Linux and UNIX) have been the trusted and proven choices for distributed COBOL application development for nearly 20 years. These classic tools enable COBOL developers to build and maintain enterprise applications. Micro Focus Net Express with.NET is the market-leading COBOL development environment for extending core business processes to the.NET Framework and other distributed platforms.
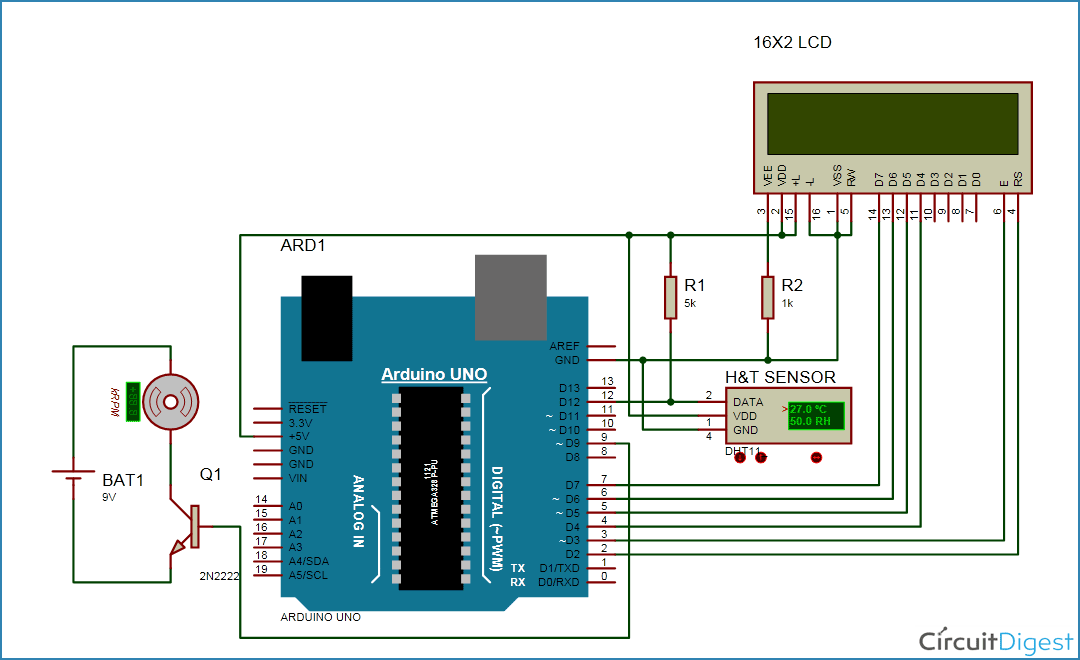
Digital Temperature Controller using arduino, here we are using arduino as main controller, this temperature controller controls the temperature of any heating device with given set points, It also displays state of the device either on or off and current temperature. As the name implies, a temperature controller is an instrument used to control temperature. The temperature controller takes an input from a temperature sensor and has an output that is connected to a control element such as a heater or fan. To accurately control process temperature without extensive operator involvement, a temperature control system relies upon a controller, which accepts a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD and LM35 as input. It compares the actual temperature to the desired control temperature, or set-point, and provides an output to a control element.
[1] Mustafa Saad, Hossam Abdoalgader, and Muammer Mohamed, “Automatic Fan Speed Control System Using Microcontroller” [2] Temperature Controlled Relay with Arduino – Tutorial #6 by electroschematics.com. Temperature Controlled Fan by using Arduino-uno It consists of automatic circuit which controlls the speed of the fan according to variation in temperature and shows result in Thingspeak 36,997 views.

What Are the Different Types of Controllers, and How Do They Work? There are three basic types of controllers: on-off, proportional and PID. Depending upon the system to be controlled, the operator will be able to use one type or another to control the process.
In this Arduino example we are making on-off type controller. On/Off Control An on-off controller is the simplest form of temperature control device. The output from the device is either on or off, with no middle state. An on-off controller will switch the output only when the temperature crosses the set-point. For heating control, the output is on when the temperature is below the set-point, and off above set-point. Since the temperature crosses the set-point to change the output state, the process temperature will be cycling continually, going from below set-point to above, and back below. In cases where this cycling occurs rapidly, and to prevent damage to relays and valves, an on-off differential, or “hysteresis,” is added to the controller operations.
This differential requires that the temperature exceed set-point by a certain amount before the output will turn off or on again. On-off differential prevents the output from “chattering” or making fast, continual switches if the cycling above and below the set-point occurs very rapidly. On-off control is usually used where a precise control is not necessary, in systems which cannot handle having the energy turned on and off frequently, where the mass of the system is so great that temperatures change extremely slowly, or for a temperature alarm.
- Author: admin
- Category: Category

Microfocus netexpress free download. Our website provides a free download of Micro Focus Net Express 5.106.79. The most popular versions among Micro Focus Net Express users are 5.1, 4.0 and 3.1. The most popular versions among Micro Focus Net Express users are 5.1, 4.0 and 3.1. Net Express® (for Windows) and Server Express™ (for Linux and UNIX) have been the trusted and proven choices for distributed COBOL application development for nearly 20 years. These classic tools enable COBOL developers to build and maintain enterprise applications. Micro Focus Net Express with.NET is the market-leading COBOL development environment for extending core business processes to the.NET Framework and other distributed platforms.
Digital Temperature Controller using arduino, here we are using arduino as main controller, this temperature controller controls the temperature of any heating device with given set points, It also displays state of the device either on or off and current temperature. As the name implies, a temperature controller is an instrument used to control temperature. The temperature controller takes an input from a temperature sensor and has an output that is connected to a control element such as a heater or fan. To accurately control process temperature without extensive operator involvement, a temperature control system relies upon a controller, which accepts a temperature sensor such as a thermocouple or RTD and LM35 as input. It compares the actual temperature to the desired control temperature, or set-point, and provides an output to a control element.
[1] Mustafa Saad, Hossam Abdoalgader, and Muammer Mohamed, “Automatic Fan Speed Control System Using Microcontroller” [2] Temperature Controlled Relay with Arduino – Tutorial #6 by electroschematics.com. Temperature Controlled Fan by using Arduino-uno It consists of automatic circuit which controlls the speed of the fan according to variation in temperature and shows result in Thingspeak 36,997 views.

What Are the Different Types of Controllers, and How Do They Work? There are three basic types of controllers: on-off, proportional and PID. Depending upon the system to be controlled, the operator will be able to use one type or another to control the process.
In this Arduino example we are making on-off type controller. On/Off Control An on-off controller is the simplest form of temperature control device. The output from the device is either on or off, with no middle state. An on-off controller will switch the output only when the temperature crosses the set-point. For heating control, the output is on when the temperature is below the set-point, and off above set-point. Since the temperature crosses the set-point to change the output state, the process temperature will be cycling continually, going from below set-point to above, and back below. In cases where this cycling occurs rapidly, and to prevent damage to relays and valves, an on-off differential, or “hysteresis,” is added to the controller operations.
This differential requires that the temperature exceed set-point by a certain amount before the output will turn off or on again. On-off differential prevents the output from “chattering” or making fast, continual switches if the cycling above and below the set-point occurs very rapidly. On-off control is usually used where a precise control is not necessary, in systems which cannot handle having the energy turned on and off frequently, where the mass of the system is so great that temperatures change extremely slowly, or for a temperature alarm.