
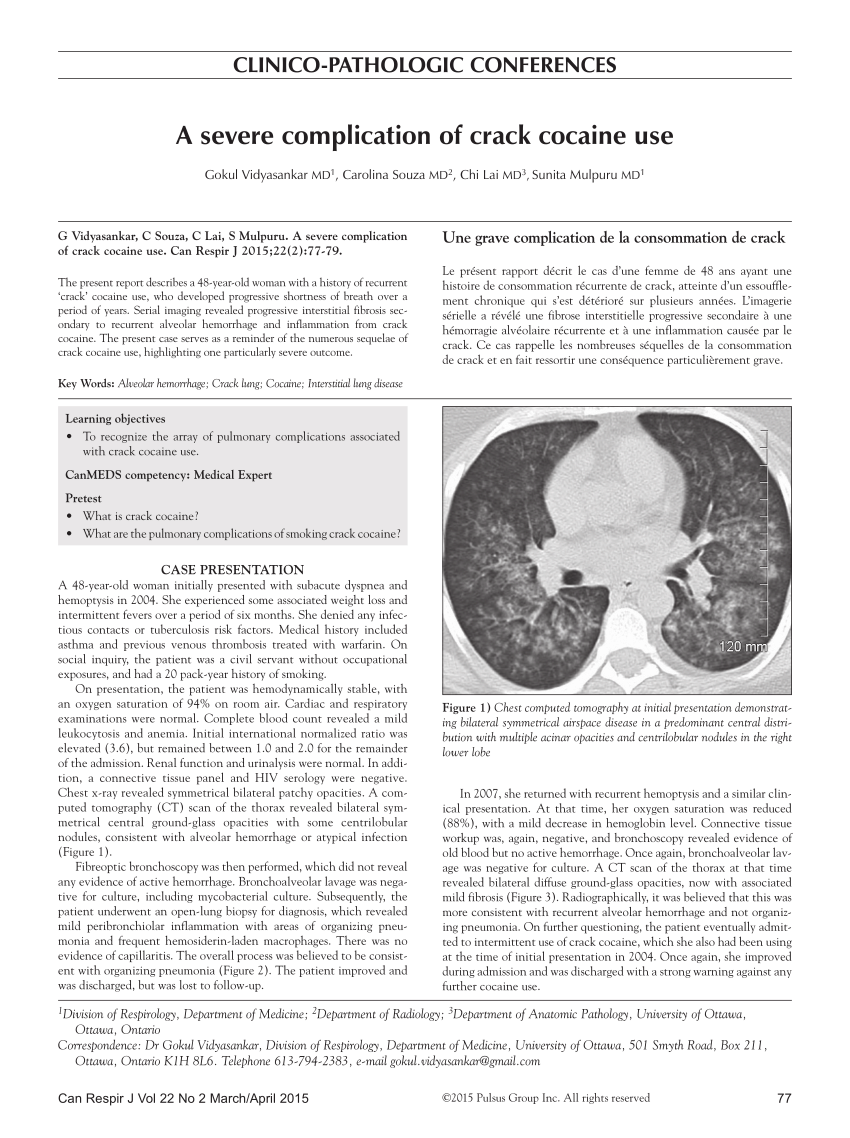
Oct 8, 2018 - I-Doser Premium – Binaural Brainwave Doses for Every Imaginable Mood. Download I-Doser Premium APK for free from Allfreeapk.com now.
Methadone is a medication used to relieve severe pain. It's also used to prevent withdrawal symptoms in people who are addicted to opiate drugs such as,,,. Dolophine and Methadose are two common brand names for methadone. Methadone is a narcotic that works by changing the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain. It was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1947. Methadone Warnings Methadone carries a black-box warning because it may cause serious or life-threatening breathing problems. The risk of breathing problems is highest during the first 72 hours of treatment and any time your dose is increased.
You should tell your doctor if you have or have ever had, slowed breathing,, or any other type of lung disease; a head injury; any condition that increases pressure in your brain; or obstructive or central. Also, you should watch for any signs of breathing problems, including slowed breathing, long pauses between breaths, or shortness of breath. This medication may also cause a rare heart problem known as a long QT interval. This condition can cause irregular heartbeat, fainting, or sudden death. You should tell your doctor if you or anyone in your family has or has ever had long QT syndrome.
Also, tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had a slow or irregular heartbeat, heart disease, or low levels of potassium or magnesium in your blood. Call your doctor right away if you experience a pounding heartbeat, lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting while taking methadone. Before taking methadone, you should tell your doctor if you have or have ever had: • Paralytic ileus (a condition where digested food doesn't move through the intestines)• A blockage in your intestine• An enlarged • Difficulty urinating• Addison's disease (a condition where the adrenal gland doesn't work properly)• Seizures•,,, liver, or kidney disease Tell your physician you are taking methadone before having any type of surgery, including dental procedures. Methadone Withdrawal If you've been using methadone regularly for several weeks or more, you may experience withdrawal symptoms when you stop taking it. Talk to your doctor before you stop using methadone.
Your doctor may advise you to gradually reduce the amount you're using, rather than stopping treatment completely, or to take another narcotic for a while, in order to reduce the risk for withdrawal. If you suddenly stop taking methadone, you may experience withdrawal symptoms, including: • Restlessness• Teary eyes• Runny nose• Yawning• Sweating• Chills• Muscle pain• Widened pupils (black circles in the middle of the eyes)• Irritability• • Backache• Joint pain• Weakness• Stomach cramps• Sleep disturbance• Nausea• Decreased appetite• Vomiting/diarrhea The Methadone 'High' and Abuse Taking large doses of methadone, like many narcotics, can cause a 'high.' However, this is an extremely dangerous practice and can lead to overdose and death. You should never take more methadone than your doctor prescribes. Methadone may be habit-forming.
Do not take larger doses of methadone or take it for a longer period of time than your doctor prescribes. You should tell your physician if you or anyone in your family has a history of drinking large amounts of alcohol, using street drugs, or having any type of mental illness. Make sure to take this drug exactly as your doctor prescribes, so you don't overdose.
 According to the Centers for Control Disease and Prevention (CDC), nearly one-third of deadly drug overdoses in the United States involve methadone. Store methadone in a safe place, so no one else can take it. Keep this drug out of the reach of children. You shouldn't stop taking methadone without first talking to your doctor. You doctor will likely want to decrease your dose gradually before taking you off this drug.
According to the Centers for Control Disease and Prevention (CDC), nearly one-third of deadly drug overdoses in the United States involve methadone. Store methadone in a safe place, so no one else can take it. Keep this drug out of the reach of children. You shouldn't stop taking methadone without first talking to your doctor. You doctor will likely want to decrease your dose gradually before taking you off this drug.
If you take methadone to help you with an opiate addiction, you must enroll in a treatment program that's approved by state and federal governments and follows specific federal laws. Ask your doctor about enrolling in such a program. Pregnancy and Methadone Methadone might harm an unborn baby.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant while taking this medicine. Your baby may also develop life-threatening withdrawal symptoms after birth if you take methadone during pregnancy.
Methadone can pass into breast milk and may harm a breastfeeding baby, so talk to your doctor before breastfeeding while taking this medication. Many medications may interact with methadone. Methadone comes as a tablet, a dispersible tablet, a liquid, a concentrated solution, or an injection. Your dose of methadone may range from 2.5 milligrams (mg) to 120 mg daily, depending on your condition. When it's used to relieve pain, the drug may be taken every eight to 12 hours. You should take methadone exactly as your doctor prescribes. Your physician might change your dose during the course of your treatment.
- Author: admin
- Category: Category
Oct 8, 2018 - I-Doser Premium – Binaural Brainwave Doses for Every Imaginable Mood. Download I-Doser Premium APK for free from Allfreeapk.com now.
Methadone is a medication used to relieve severe pain. It's also used to prevent withdrawal symptoms in people who are addicted to opiate drugs such as,,,. Dolophine and Methadose are two common brand names for methadone. Methadone is a narcotic that works by changing the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain. It was first approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1947. Methadone Warnings Methadone carries a black-box warning because it may cause serious or life-threatening breathing problems. The risk of breathing problems is highest during the first 72 hours of treatment and any time your dose is increased.
You should tell your doctor if you have or have ever had, slowed breathing,, or any other type of lung disease; a head injury; any condition that increases pressure in your brain; or obstructive or central. Also, you should watch for any signs of breathing problems, including slowed breathing, long pauses between breaths, or shortness of breath. This medication may also cause a rare heart problem known as a long QT interval. This condition can cause irregular heartbeat, fainting, or sudden death. You should tell your doctor if you or anyone in your family has or has ever had long QT syndrome.
Also, tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had a slow or irregular heartbeat, heart disease, or low levels of potassium or magnesium in your blood. Call your doctor right away if you experience a pounding heartbeat, lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting while taking methadone. Before taking methadone, you should tell your doctor if you have or have ever had: • Paralytic ileus (a condition where digested food doesn't move through the intestines)• A blockage in your intestine• An enlarged • Difficulty urinating• Addison's disease (a condition where the adrenal gland doesn't work properly)• Seizures•,,, liver, or kidney disease Tell your physician you are taking methadone before having any type of surgery, including dental procedures. Methadone Withdrawal If you've been using methadone regularly for several weeks or more, you may experience withdrawal symptoms when you stop taking it. Talk to your doctor before you stop using methadone.
Your doctor may advise you to gradually reduce the amount you're using, rather than stopping treatment completely, or to take another narcotic for a while, in order to reduce the risk for withdrawal. If you suddenly stop taking methadone, you may experience withdrawal symptoms, including: • Restlessness• Teary eyes• Runny nose• Yawning• Sweating• Chills• Muscle pain• Widened pupils (black circles in the middle of the eyes)• Irritability• • Backache• Joint pain• Weakness• Stomach cramps• Sleep disturbance• Nausea• Decreased appetite• Vomiting/diarrhea The Methadone 'High' and Abuse Taking large doses of methadone, like many narcotics, can cause a 'high.' However, this is an extremely dangerous practice and can lead to overdose and death. You should never take more methadone than your doctor prescribes. Methadone may be habit-forming.
Do not take larger doses of methadone or take it for a longer period of time than your doctor prescribes. You should tell your physician if you or anyone in your family has a history of drinking large amounts of alcohol, using street drugs, or having any type of mental illness. Make sure to take this drug exactly as your doctor prescribes, so you don't overdose.
 According to the Centers for Control Disease and Prevention (CDC), nearly one-third of deadly drug overdoses in the United States involve methadone. Store methadone in a safe place, so no one else can take it. Keep this drug out of the reach of children. You shouldn't stop taking methadone without first talking to your doctor. You doctor will likely want to decrease your dose gradually before taking you off this drug.
According to the Centers for Control Disease and Prevention (CDC), nearly one-third of deadly drug overdoses in the United States involve methadone. Store methadone in a safe place, so no one else can take it. Keep this drug out of the reach of children. You shouldn't stop taking methadone without first talking to your doctor. You doctor will likely want to decrease your dose gradually before taking you off this drug.

If you take methadone to help you with an opiate addiction, you must enroll in a treatment program that's approved by state and federal governments and follows specific federal laws. Ask your doctor about enrolling in such a program. Pregnancy and Methadone Methadone might harm an unborn baby.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant while taking this medicine. Your baby may also develop life-threatening withdrawal symptoms after birth if you take methadone during pregnancy.
Methadone can pass into breast milk and may harm a breastfeeding baby, so talk to your doctor before breastfeeding while taking this medication. Many medications may interact with methadone. Methadone comes as a tablet, a dispersible tablet, a liquid, a concentrated solution, or an injection. Your dose of methadone may range from 2.5 milligrams (mg) to 120 mg daily, depending on your condition. When it's used to relieve pain, the drug may be taken every eight to 12 hours. You should take methadone exactly as your doctor prescribes. Your physician might change your dose during the course of your treatment.