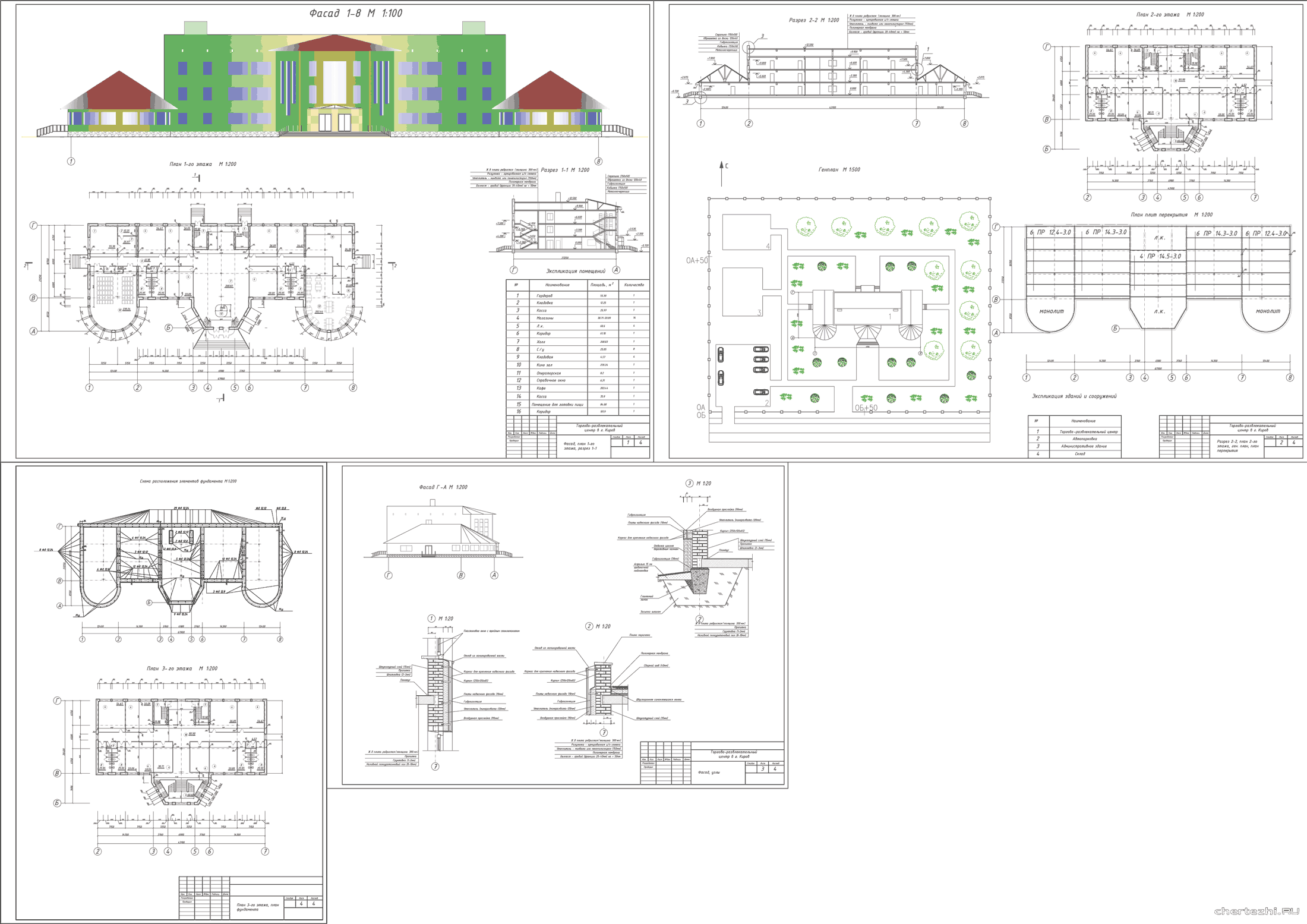

To Create 3D Inventor Models of 2D DWG Underlay Layouts. Products and versions covered. Factory Design Suite 2018, Inventor 2018, & Product Design Suite 2018. 0 contributions. In-Product View. ADD TO COLLECTION. The DWG file format is used in 3-dimensional drawing and design programs, such as AutoDesk AutoCAD. Using a vector-based graphics program, such as the commonly-used Adobe Illustrator, or a direct conversion program, you can convert a DWG file to Encapsulated PostScript (EPS).

Create 3D Inventor parts associative to the source 2D geometry created in AutoCAD. • Insert an AutoCAD DWG file as an associative DWG: • In a part file: • Manage tab Insert panel Import • 3D Model tab Create panel Import • In an assembly file: • Assemble tab Component panel Place • In the Place Component dialog box, select a DWG file and click Open.
For more information see • In a 2D sketch, click a face or work plane to set the sketch plane. • Click Sketch tab Create panel Project DWG Geometry.
• Select the geometry to project. Select one of 3 options: • Single geometry • Connected geometry: Closed loop and/or open loop. • Geometry block. Note: You can project DWG geometry in another part that is also open for edit in an assembly.
 • When done, select Cancel or right-click and select OK. • On the 3D Model tab, extrude the DWG geometry and create 3D features as desired. • In an assembly file, you can use the Joint, Constrain, and Assemble commands to create relationships between a DWG underlay block and a part.
• When done, select Cancel or right-click and select OK. • On the 3D Model tab, extrude the DWG geometry and create 3D features as desired. • In an assembly file, you can use the Joint, Constrain, and Assemble commands to create relationships between a DWG underlay block and a part.
You can work on DWG geometry in an assembly file at the same time as working on the same DWG geometry in a part file. When changes are made to projected DWG geometry in a part file, the corresponding DWG geometry in the assembly file is updated with these changes.
The projection associativity will be kept even when the DWG is modified. For example: • Insert a part (PART A) that has AutoCAD 2D geometry into an assembly and save the file. • In a new part file (PART B): Create a sketch and project the DWG geometry from PART A into PART B. The projection associativity will be kept even the DWG is modified.
When the original DWG file is updated in AutoCAD, the corresponding Inventor files will be updated accordingly, either for geometry change or position change.
You can link or import dwg files into revit files (Insert/Link CAD), but they will simply be background linework which doesn't really gain you anything over just having a dwg file. If they are floor plans, etc you can trace over them with walls & doors to truly make them useful in Revit. Of course you will need level/3d information as well. If you are talking details, etc, you can import them into views or families, but in the long run it's much better to trace them into native revit linework/hatch areas as dwgs tend to negatively impact revit file performance. For details, first convert all linework to a single ACAD layer, then purge all unused layers. Import the.dwg into a drafting view in a Revit project created only for the purpose of converting details.
- Author: admin
- Category: Category

To Create 3D Inventor Models of 2D DWG Underlay Layouts. Products and versions covered. Factory Design Suite 2018, Inventor 2018, & Product Design Suite 2018. 0 contributions. In-Product View. ADD TO COLLECTION. The DWG file format is used in 3-dimensional drawing and design programs, such as AutoDesk AutoCAD. Using a vector-based graphics program, such as the commonly-used Adobe Illustrator, or a direct conversion program, you can convert a DWG file to Encapsulated PostScript (EPS).

Create 3D Inventor parts associative to the source 2D geometry created in AutoCAD. • Insert an AutoCAD DWG file as an associative DWG: • In a part file: • Manage tab Insert panel Import • 3D Model tab Create panel Import • In an assembly file: • Assemble tab Component panel Place • In the Place Component dialog box, select a DWG file and click Open.
For more information see • In a 2D sketch, click a face or work plane to set the sketch plane. • Click Sketch tab Create panel Project DWG Geometry.
• Select the geometry to project. Select one of 3 options: • Single geometry • Connected geometry: Closed loop and/or open loop. • Geometry block. Note: You can project DWG geometry in another part that is also open for edit in an assembly.
 • When done, select Cancel or right-click and select OK. • On the 3D Model tab, extrude the DWG geometry and create 3D features as desired. • In an assembly file, you can use the Joint, Constrain, and Assemble commands to create relationships between a DWG underlay block and a part.
• When done, select Cancel or right-click and select OK. • On the 3D Model tab, extrude the DWG geometry and create 3D features as desired. • In an assembly file, you can use the Joint, Constrain, and Assemble commands to create relationships between a DWG underlay block and a part.
You can work on DWG geometry in an assembly file at the same time as working on the same DWG geometry in a part file. When changes are made to projected DWG geometry in a part file, the corresponding DWG geometry in the assembly file is updated with these changes.
The projection associativity will be kept even when the DWG is modified. For example: • Insert a part (PART A) that has AutoCAD 2D geometry into an assembly and save the file. • In a new part file (PART B): Create a sketch and project the DWG geometry from PART A into PART B. The projection associativity will be kept even the DWG is modified.
When the original DWG file is updated in AutoCAD, the corresponding Inventor files will be updated accordingly, either for geometry change or position change.
You can link or import dwg files into revit files (Insert/Link CAD), but they will simply be background linework which doesn't really gain you anything over just having a dwg file. If they are floor plans, etc you can trace over them with walls & doors to truly make them useful in Revit. Of course you will need level/3d information as well. If you are talking details, etc, you can import them into views or families, but in the long run it's much better to trace them into native revit linework/hatch areas as dwgs tend to negatively impact revit file performance. For details, first convert all linework to a single ACAD layer, then purge all unused layers. Import the.dwg into a drafting view in a Revit project created only for the purpose of converting details.